Ancient Egypt Religion Facts
The Egyptian religion was practiced for more than 3 millennia and they believed in various gods.
The Egyptian religion, moreover, considered certain animals sacred, such as the cat, the hawk, the scorpion, the lion, the serpent, the cow, the beetle, the bull, the ibis and the crocodile.
They performed sacred cults to prevent the gods from getting angry or offended.
The figure of the Gods was represented on Earth by a pharaoh who had divine blood. The pharaoh was the divine heir of the Gods and his mandate lasted all his life.
They firmly affirmed the immortality of the soul and based, for that, on mummification.
1- Polytheistic
The ancient Egyptians believed in several Gods. At first these were animal (zoomorphic) but then over the years were modifying their drawings and attributing them semi-human form.
These gods intervene in the lives of human beings on a daily basis and informed the Pharaohs what they should do.
2- Offerings
It was the form of worship on the part of the Egyptian civilization towards their Gods. These offerings were carried out in the temples.
3- Amulets
These objects used by both the living and the dead. Amulets provided protection and powers. That way they could attract love, health, work, money, etc.
Sometimes these amulets were made of precious or semiprecious stones and hung from their necks, wrists or hiding them in their clothes.
Sometimes they hid them in small boxes and carried them permanently. Some of the best known amulets were: Ankh “the key to life” or royal vulture.
4- Worship
The temple was the first place of worship. This place was the place or House of the Gods. Inside, there were different rooms with corridors and even some passages. The whole temple is a great key or path for the soul to reach the afterlife.
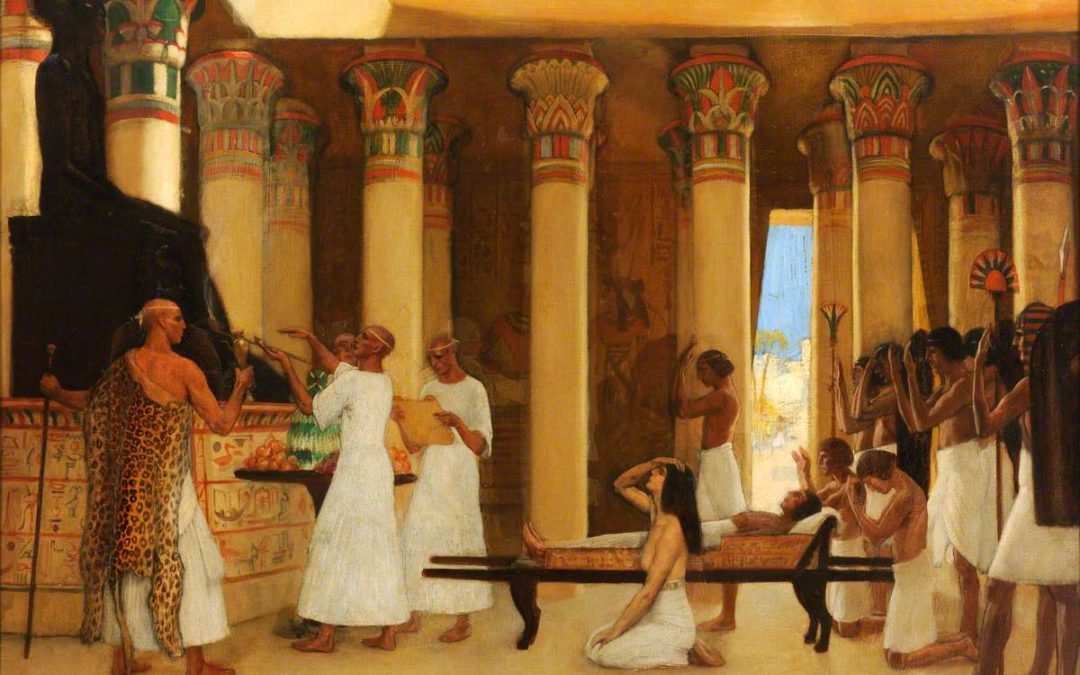
Inside the tombs food was placed so that the soul could have food on its journey. One of their beliefs was the mummification of the dead as part of the eternal journey of the soul into the afterlife.
This mummification was done by the priests. After the mummification would be the “judgment of the dead”. This trial was the most important event for the dead. All the actions performed by the deceased in lifetime would be evaluated there.
5- Mummification
The process of mummification consisted in the removal of the vital organs (which were then placed in sacks called Canopic jars) and the washing of the body. In this practice resin or balsam was used.
The purpose was to avoid the putrefaction of the body. In this way the body would be ready for its journey and encounter with the soul in the afterlife.
6- Categories of Gods
Within this religion there are different ranks or hierarchies of the Gods.
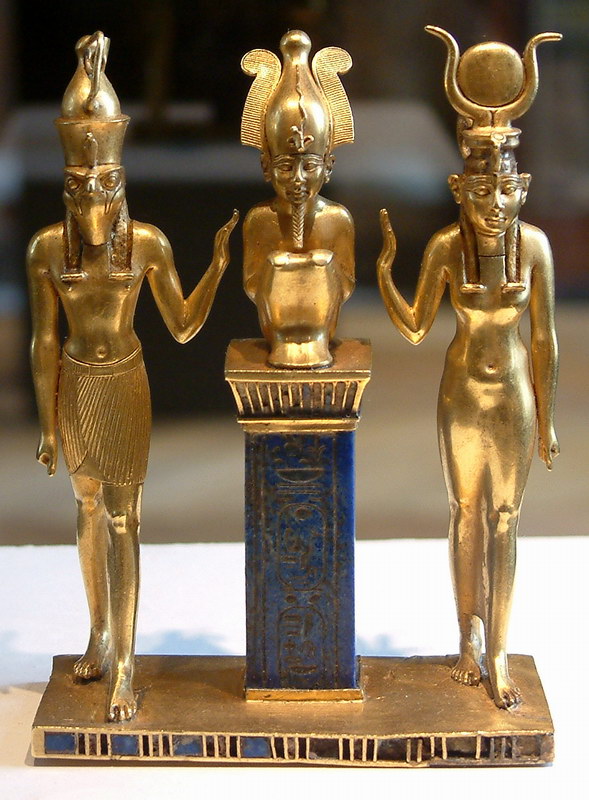
Thus were national Gods like Amun (God of Light and Air) Osiris (God of life, fertility and after death), Isis (the wife of Osiris, was the goddess of the moon), Horus (God of the heavens), Ra (God of the sun and supreme creator), Anubis, Thoth and Seth but there were also local gods.
7- Pharaoh’s functions
According to what it is known by writings and symbols Osiris had left the royalty of the world to his son Horus. This was the father of all the pharaohs of the earth.
For that reason the kings (pharaohs) and their descendants had divine blood.
For this reason the ancient Egyptian pharaohs married between brothers and cousins with the aim of maintaining the purity of the blood.
The first-born of the royal family would be the divine heir, although this had to be approved by the Gods.
The role of the pharaoh was to be a God and govern men on earth. Once a pharaoh died a temple was built for him.
8- The judgment of the dead
This judgment was presided over by Osiris, Ra and 40 other Gods. During the trial, every action that the deceased would have done in life would be evaluated.
The balance of guilt or salvation (exerted by Thoth) would determine whether the dead man was worthy of eternal life or whether he would lose his soul.
In case of the loss of his soul it was destroyed by Ammit. Ammit who was part hippopotamus, part lion, and part crocodile,the three largest “man-eating” animals known to ancient Egypt religion. Otherwise he would live in the presence and company of the Gods with all happiness during eternity.
9- The book of the dead
This is a funerary book. It was inside the tombs to help the deceased on his journey after death. The book indicated how the dead man could evade the terrible dangers that awaited him after he died.
Only with the help of the book could the deceased face the judgment of Osiris and save his soul from destruction.
This book was written on papyrus and was detailed by hieroglyphics and iconography in tombs and coffins.
10- The myth of Osiris and Isis
Osiris was the God of fertility. He ruled with Isis in ancient Egypt. But Seth, brother of Osiris, was jealous of such a situation and looked for a way to get rid of his brother.
So he made a gold coffin, locked it to Osiris and threw the sarcophagus into the Nile River.
Then Isis looked for the coffin tirelessly until she found it. This led him to the pantheon, since only there would he be safe.
However, the myth indicates that Seth found the coffin, opened it and removed the body of his brother and splitting it in 14 parts that scattered throughout Egypt.
After these events Isis traveled all over Egypt until she found the 14 pieces and, with the help of Anubis, reconstructed the immortal body of Osiris.