Ancient Egypt civilization: One of the ancient societies with the best documentation the world ever has known, day to day living of Egyptian is well described.
One thing particular to human beings is a particular way of life and a particular way of doing things.
How did Egypt start as a civilization?
This in a way can be similar to other societies’ life pattern or may be dissimilar. So also has culture been part of the Nile valley as far back as 6000 BC. This period is before Ancient Egypt was civilized in 3000 BC.
At this time, king Narmer gathered all societies that surround the Valley of Nile and whichever emerges will continue to grow for millennia.
This continues till the time Egypt experienced the struggle of colonization in the hands of the Roman Empire.
Which river shaped ancient Egyptian civilization?
The river Nile was of great importance in the civilization of the ancient Egyptians. Without this river, they would not exist or produce great wonders as we have known it.
As one of the famous rivers, it was the life of the people. They were influenced by the rise and fall of the river Nile to view the cycles of death and birth and rebirth.
This made them believe in the afterlife and therefore, they elaborate their rituals for their dead relatives, especially the nobles and the royalties.
They prepare for their dead according to rituals and they made monuments for their dead as well.
The river Nile was the center of the ancient Egypt. It made transportation to and fro the land of Egypt without stress.
It made it easy to move towards the sub-Saharan African and north to make trading easy.
The knowledge of the ancient Egyptians way of life is built around the discoveries of the archaeologists since the early period of the 19th century.
These discoveries had presented us with evidence that made picturing and gaining an understanding of the people’s culture easy despite the differences it has with the new age culture.
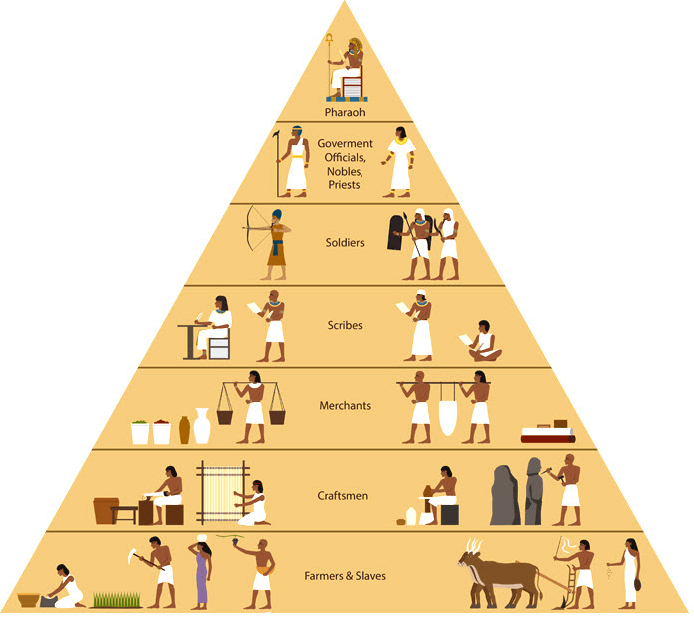
Society in Ancient Egypt
The Greek scholar, Herodotus, in his scholar write-up as regards histories exclusively about ancient Egypt set between 664 BC and 525 BC.
This material has been valuable for to our records of the everyday life of the ancient Egyptians.
In his writing, he says “Concerning Egypt itself, I shall extend my remark to a great length because there is no country that possesses so many wonders, nor any that has such a number of work which defies description…” truly, he must have seen a lot of intriguing things which his artwork covers.
As regards the society and its social shape of historical Egypt, we must think about a culture that spanned 3,000 years, reaching from the predynastic duration through to the time of Ptolemy.
In the course of the three millennia of this period, we are capable of identifying five key factors that shape our knowledge of the society:
kinship (connection between blood family and thru marriage), region (connection among humans born within the identical place or who live inside the identical place), gender (connection among people of the same sex and sexual orientation), age (connection among humans of the equal age), and social beauty (connection among human beings born into the equal social repute).
On the very highest rank of the social ladder, the Egyptian pharaoh was seen as a residing god, especially a manifestation of the earthly embodiment of Horus, the god of order, the son of the goddess Isis.
The pharaoh took the chargeable position of keeping order and ensuring that the gods had been kept glad about human endeavor.
It’s additionally not surprising that the pharaoh’s pastimes and obligations protected military campaigns.
The women that surround the king, that is, the wives, mothers, and daughters of the king are given great accolades and highly respected.
One of the popular and most talked about marriage of a royal home was that of Akhenaten and Nerfititi.
The name of a king’s wife would be represented in the cartouches that dated to the Second Intermediate Period.
Several numbers of the kings’ wives were given a final resting place and buried in a great pyramid.
After the pharaoh on the social pyramid is the elites which comprised the nobles and the priests of the land.
For some elites, they have family connections with the ruling government, however, not all elites had family connections with the monarch.
A typical example of the elites without family connection with the monarch is Imhotep.
He was an educated elite, a scribe. He was educated in arithmetic, architecture, and writing and in medicine. He eventually rose to become to Djoser, an adviser.
The youngsters of the high-class authorities and officials in ancient Egypt would expect a unique kind of upbringing, treatment, and lifestyles in comparison to the child of any other social class under them on the social hierarchical rank.
Usually, Egyptian writing was made from the elite magnificence and end up being the reflection of their life reviews.
The elite are followed by the craftsmen and physicians of Egyptian society – these comprised what we’d in recent times keep in mind the middle class.
After the craftsmen and the physician, the manual laborers followed. They were seen as less worthy of appreciation other than doing artworks that involved writing or mathematics.
At the bottom rung of the social order was the farmers – the class that comprised most of the general public in historic Egypt.
Their lives are hardly ever recorded in extant Egyptian writings. However, their lives via archaeological work on funerary devices have been developed.
Those who are given the least part of the social hierarchy in the society are the slaves. Even though they are the least in the society, they play a very vital role in the lives of those who occupied the high positions in the society.
The lifestyle of the Ancient Egyptians did not embrace the concept of freedom as we do in this modern age.
Even though there are classes to bring about differences between the Egyptians, the women enjoy some kind of rights many cultures do not accord their women.
They had the right to marry anyone they wish, but lands and to divorce. Though this right did not stop the men from being the head of the family.
When the father died, the eldest male son became the head of the family. So, women in ancient Egypt enjoyed great freedom.
Ancient Egyptian Daily Life
The society of the Egyptian is a true depiction of a classy environment. While some people belong to the high class, some to the middle class and some other ones are in the lower class.
As much as their activities depict their social class, so also do their home depict what class they belong.
An ordinary Egyptian, especially the farmers who are seen as the lowest class in the hierarchical order, they do not have a slave to help in preparing their day.
The wife of the ordinary man is saddled with the responsibility of cooking and preparing the children for the day. They use a bench to eat and the family sits on the mat.
The farmer would go to his farm to toil while the wife remained at home all day doing the chores, such as tidying up the home, washing and also preparing food for the evening.
All they have to eat is bread and fruit and the man sometimes consumed beer to shove the day’s stress. Also, after harvest, the farmer is to pay for using the temple land with some of the products harvested.
On the other hand, the noble’s home is another world on its own. The day to day activities is done by the slaves. The slaves help the man in washing and shaving in order to prepare for the day ahead.
In most cases, the wife would have a slave to assist her personally, apart from the one the husband owns. These slaves are also different from the ones that prepare the children for the day.
In a royal home, each child has a slave to him or herself. A nobleman would also hire someone to help to watch over his land.
Their homes were made from papyrus and mud which were gotten close to the river. The river Nile produced them to make life easier for the ancient Egyptian.
However, as time went on, the climatic condition made it hard to live in a house made from Papyrus and mud. They then start making bricks from mud and clay to withstand flood that came yearly.
The lower class men lived in a humble abode of single rooms with their children, decorated with mats and probably a single stool.
To keep the room lit, they used a mat on the windows. In contrast, the upper-class occupants could as many rooms as possible.
They ensure their homes had space in its garden in order to host guests for whatever occasion.
For a typical Ancient Egyptian, they enjoy an extended family life, especially in the rural areas. The urban part, however, has their homes close to each other.
They mostly used their ground floor for business while the upper part of the house is used as the home.
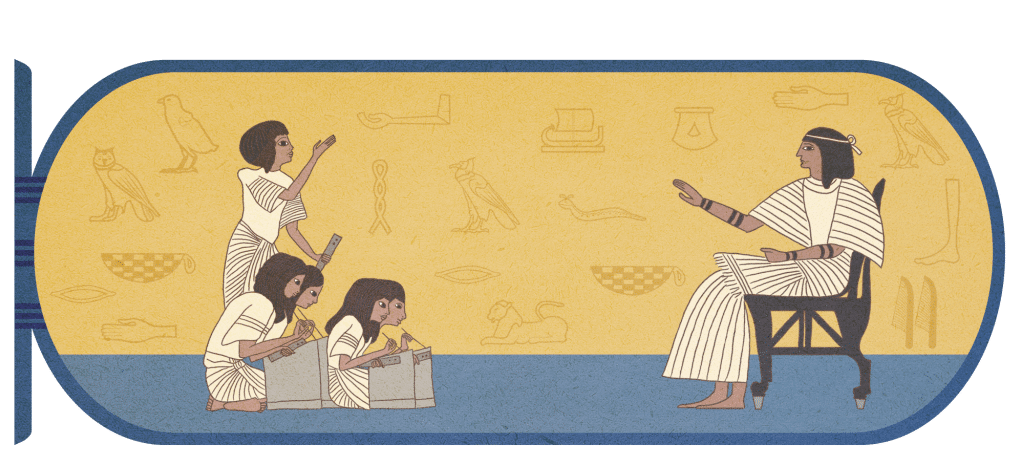
Education in Ancient Egypt
One of the instruments that made people emerge and climb the social rank of education. During the Ancient times, it is seen as the way of improving one’s status.
More so, it is a major part of the elites’ children lifestyle while the children of the lower class if a male follows the father to work and the girl child sit with the mother to learn to do the domestic chores at home.
Also, it can be said to be a way of gathering the knowledge about the world.
The basics of education started with the family units. The children learn and develop their value system from their family, their parents to the precise.
The males are trained in whatsoever work that caught their interest. This could be agriculture, crafting, medicine, administration or architectural work.
However, the female is not given this kind of opportunity. Education is therefore passed down in form of imparting morals into the younger generations.
What Ancient Egypt refers to as education is contained in the Books of instruction which gives an interesting insight into the different social life and the right behavior expected.
Many of the Egypt boys were trained to be scribes in the school at Thebes. However, not all benefited from the opportunity to be educated, only a minority had access to education.
In the school, the students were taught history and literature. They were also trained in the disciplines that are related to surveying, military endeavor, accounting and architectural work.
There were journals of the American Oriental Societal that talked about the Egyptian students.
Siculus who went to Egypt in 60-57 BC noticed that the students had “strong bodies and with spirits capable of leadership and endurance because of their training in the finest habits”.
Another scholar named Diodorus also noticed note that the students that learned scribbling learned two types of writing, ” one which is called ‘sacred’ and one that is widely used for instruction.”
Ancient Egypt Religion
The ancient Egyptians had and served several gods and goddesses. To them, the most important god was Ra, the god of the sun.
He was prayed to for good harvests. The famous goddess and most served too in Egypt was Isis. She was seen as the ideal wife and mother.
Her husband was Osiris, the ruler of the dead. She is also the mother of the god of order, Huros.
Most of the Ancient Egyptians prayed to the gods in their homes. The gods’ abode was in great temples. The famous one is located at Karnak and it consists of more than 130 columns that are 25 meters high.
The Ancient Egyptians believed in the afterlife. They, therefore, made rituals for their dead and preserve them in mummies so as to ensure they do not decay.
These mummies were then let down into the tomb. They provide food, clothing and some other items, in case of royalties, they put gold and some treasures in the tomb so that the dead would not be in need in the afterlife.
They also made pictures of the person’s daily life on the wall of the person’s tomb wall.
In conclusion, the Ancient Egyptians culture is full of wonders. Their society and social structure, home, education, and religion are worth given attention to.
Even though their lifestyle is quite different from the modern age’s culture, however, their culture is fascinating.
Working life in Ancient Egypt
Historian J M Roberts wrote that “ancient Egypt has always been our finest seen inheritance from antiquity.” as such, the archaeology and scholarship that has ultimately advanced around ancient Egypt gives us a feel of both the massive and small photograph of the nation.
Social position, then, changed into connected with one’s profession: a relationship that echoes and anticipates what nonetheless holds genuine for so many in the twenty first century round the sector.
Whilst was the final time you went to a get together and weren’t requested what work you do to make a living?
It’s important to make clear the factor that agricultural working life turned into the broad base on which Egyptian society and culture became built.
Inside the Early Dynastic duration and thereafter, farmers lived in small villages and cereal agriculture turned into the maximum crucial home product.
Key agricultural crops were emmer wheat and barley. Of their improvement of generation and the agricultural industry, Egyptian farmers evolved irrigation systems that improved the quantity of land that could be farmed past instantaneous proximity to the River Nile.
Wine was another key agricultural product, and it became not only grapes that have been used to provide it: farmers also made wine from figs, dates and pomegranates.
Commonplace to all farming lifestyles have been sheep and goats, and wealthier farmers might also own livestock and oxen that would be a supply of food in addition to used for ploughing.
Important to the planning of the country and its people had been the scribes.
For a scribe, their habitual work could encompass writing up statistics about taxes, developing and administrating census lists and drawing up calculations for the varied, enormous building schemes throughout the kingdom.
Egypt was certainly a kingdom of grand designs. The culture of a civil provider is a long-standing function of so many nations.
Historian Dr Gae Calendar has made the point that “the Middle kingdom was a time while art, architecture and religion reached new heights however, primarily, it become an age of self belief in writing, absolute confidence encouraged by the increase of the ‘middle class’ and the scribal region of society”.
Labor-intensive mission on public buildings and monuments turned into a consistent characteristic of working life for many Egyptians, and this will have been supervised with the aid of the scribes, whose schooling covered sustained look at of administrative tactics and ideas of structure and math.
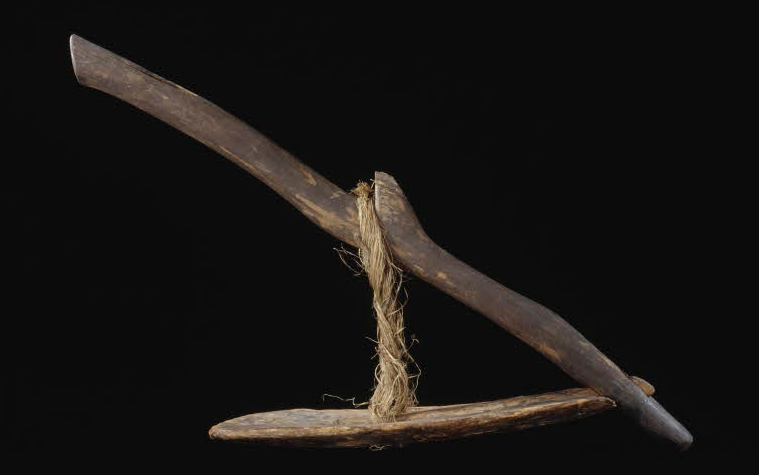
In ancient Egypt, winches, pulleys, blocks or tackle have not been applied in civil engineering enterprise.
Alternatively, levers and sleds and using enormous ramps of earth were the combinations of ‘hardware’ that allowed for tremendous portions of stone to be moved and located.
It might be fair to mention that the Hollywood movie The Ten Commandments recreates this type of interest pretty faithfully.
Historical Egypt, not like its eastward neighbor of Mesopotamia (modern-day Iran), did no longer become so urbanized and, consequently, working life for maximum of the population was largely centered around agricultural work.
Arguably, while slavery did have a key position inside the social hierarchy of ancient Egypt, it became not as usual as may be located in different cutting-edge societies beyond that of Egyptian borders.
Significantly, women, while having no longer been officially knowledgeable, worked at all standard of society, and shared nearly all of the same legal entitlements as men, from acting the responsibilities of a royal household proper through to piloting boats at the Nile and working as marketplace buyers.
Crucially, women from the higher class served in the priesthood, regularly as enchantresses, a very high-profile and resonant position in this sort of incredibly devout community.
Key to Egyptian working lifestyles became trade both inside and beyond its borders. Debate maintains about whether or not the trade benefited the working man or the pharaoh extra.
Due to the Nile main so without difficulty to the Mediterranean, Egypt ought to exchange extraordinarily easily with the Mediterranean nations.